Battery
Sealed Maintenance Free (SMF) Batteries

We offer a wide range of Sealed Maintenance Free (SMF) Batteries, designed for both two-wheelers and four-wheelers. These batteries require no water top-up and come completely sealed, ensuring a hassle-free and clean performance.
SMF batteries are more compact and efficient than conventional batteries because the electrolyte is present in a gel form, filling the plates evenly. This design increases energy density while reducing overall size.
Since the electrolyte is filled only once during factory activation, there are no filler caps. Instead, the battery is permanently sealed with a specialized plug. Additionally, SMF batteries do not require a vent tube, as the internal system is designed to recombine gases safely within the battery.
- Fully Sealed & Maintenance Free
- Lead-calcium technology
- Good charge acceptance
- High corrosion resistance
- Higher cold cranking start up
- High vibration resistance
- Spill-Proof
- Higher performance/capacity plus
- Factory charged ready to use
- Low self discharge
- Improved safety
- Leakage proof
- Extdeme durability
- Absolute safety and convenience
- Hassle-free installation and use
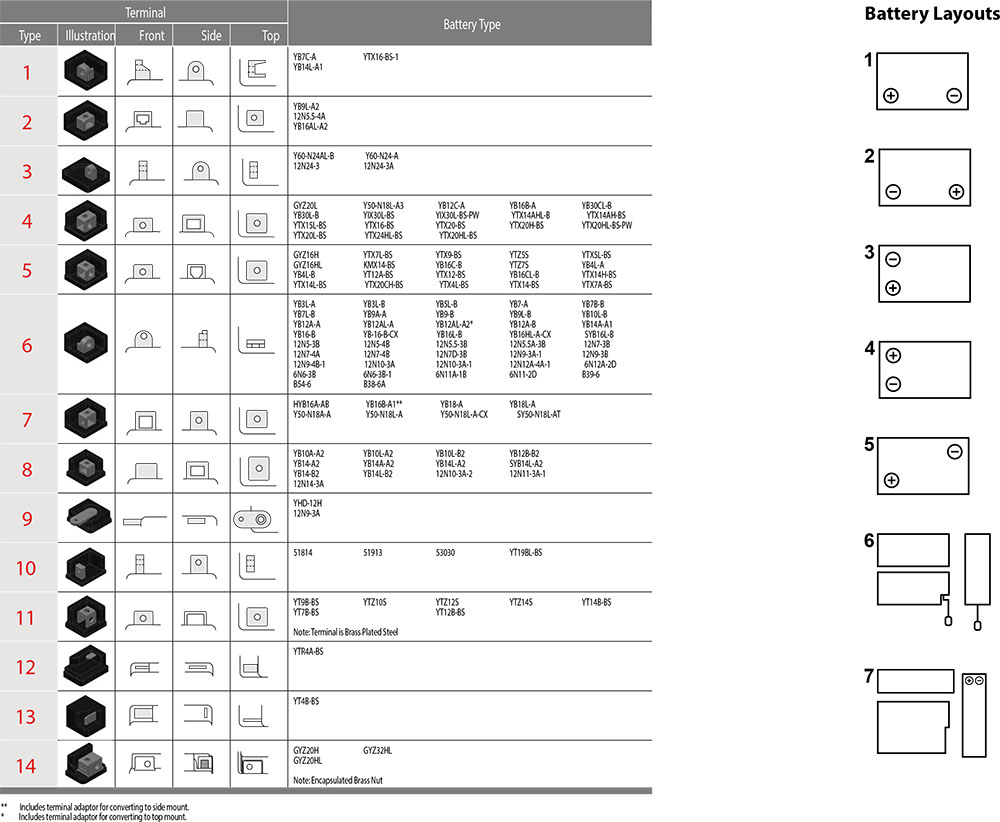
| S.no. | Model | Terminal | VoltaYe(V) | Capacity(Ah) | L(mm) | W(mm) | H(mm) |
| 1 | 6N4-2A-4 | 6 | 4 | + ,- | 71 | 71 | 96 |
| 2 | 12N5-3B | 12 | 5 | -, _ | 120 | 61 | 130 |
| 3 | YB5L-BS | 12 | 5 | -, _ | 120 | 61 | 130 |
| 4 | YB7B-B | 12 | 7 | +, – | 150 | 60 | 130 |
| 5 | 12N7A-3A | 12 | 7 | -, + | 150 | 60 | 130 |
| 6 | 12N7-3A | 12 | 7 | -, + | 137 | 77 | 126 |
| 7 | 12N7-4B | 12 | 7 | +,- | 137 | 77 | 126 |
| 8 | 12N7-3B | 12 | 7 | -,+ | 137 | 77 | 126 |
| 9 | 12N9-4B | 12 | 9 | +, – | 137 | 77 | 136 |
| 10 | 12N9-4B-1 | 12 | 9 | +, – | 133 | 77 | 136 |
| 11 | 12N9-BS | 12 | 9 | +, – | 133 | 77 | 136 |
| 12 | 12N9-3B | 12 | 9 | +, – | 133 | 77 | 136 |
| 13 | YB2.5L-BS | 12 | 2.5 | -,+ | 80 | 77 | 105 |
| 14 | YTX3L-BS | 12 | 3 | -,+ | 98.5 | 56 | 109 |
| 15 | YT4L-BS | 12 | 4 | -,+ | 114 | 70 | 85 |
| 16 | YTX4L-BS | 12 | 4 | -,+ | 114 | 70 | 85 |
| 17 | YTZ5S-BS | 12 | 4 | -,+ | 114 | 70 | 85 |
| 18 | YTZ7S | 12 | 5 | -,+ | 114 | 70 | 105 |
| 19 | YTX5L-BS | 12 | 5 | -,+ | 114 | 70 | 105 |
| 20 | YT5AL-BS | 12 | 5 | -,+ | 114 | 70 | 105 |
| 21 | YB6.5L-B | 12 | 6.5 | -,+ | 139 | 66 | 100 |
| 22 | 12N6.5L-BS | 12 | 6.5 | -,+ | 139 | 66 | 100 |
| 23 | YTX7A-BS | 12 | 7 | +,- | 150 | 87 | 93 |
| 24 | YTZ10 | 12 | 8 | +,- | 150 | 87 | 93 |
| 25 | YTX7L-BS | 12 | 7 | -,+ | 114 | 70 | 130 |
| 26 | YTX12A-BS | 12 | 10 | +,- | 150 | 87 | 105 |
| 27 | YTX9-BS | 12 | 9 | +,- | 150 | 87 | 130 |
| 28 | YTX12-BS | 12 | 2 | +,- | 150 | 87 | 145 |
| 29 | YTX14-BS | 12 | 14 | +,- | 152 | 87 | 145 |
| 30 | YTZ14 | 12 | 11 | +,- | 150 | 87 | 110 |
Sealed Battery Charging Procedure
Please follow the steps below to ensure safe and proper charging:
- Connect the Charger Correctly: Attach the cables to the battery terminals before switching on the charger.
-
Red cable → Positive terminal (+)
-
Black cable → Negative terminal (-)
-
- Voltage Limit for SMF / Gel Batteries: Do not charge Gel or SMF batteries above 14.4V, as higher voltage may cause damage.
- Start with Low Amperage: For best results, begin charging at low current output, or refer to the battery manufacturer’s recommended charging amperage.
- Perform a Load Test: Load test the battery at 3 times its Ah (Ampere Hour) rating for 15 seconds, or use an automatic battery tester to check battery health. Then, verify the voltage reading.
- Check Voltage: A healthy 12V battery should measure minimum 12.4V after testing.
- Battery Ready for Use: Once the battery holds 12.4V or more, it is ready to be installed and used.
- If Voltage is Low: If the voltage is below 12.4V or the battery fails the test, repeat the charging cycle and retest until the battery reaches the required voltage level.
Key Features of Motofine Sealed Batteries
Sealed Construction
Our advanced casing and sealing technology ensures zero electrolyte leakage from either the battery case or terminals, providing clean, safe, and reliable performance.
Electrolyte Suspension System
Motofine batteries use a micro-glass mat electrolyte suspension system that holds the maximum amount of electrolyte within the separator material.
There is no free liquid electrolyte, eliminating spills and ensuring improved vibration resistance—without the use of gels or added chemicals.
Oxygen Recombination Technology
Engineered with modern oxygen recombination technology, Motofine batteries do not require periodic topping-up with distilled water under normal operating conditions.
This results in cleaner use and extended performance life.
Low Maintenance Operation
Thanks to the sealed design and internal gas recombination, the battery operates with minimal maintenance, making it ideal for both everyday and heavy-duty applications.
Battery Safety & Handling Guidelines
Batteries must always be handled with care. During charging, batteries can release combustible gases and contain corrosive sulfuric acid, which can be harmful if mishandled. Follow the precautions below to ensure safe operation at all times.
Safety Precautions
- No Flames or Sparks: Avoid smoking, open flames, or sparks near the battery. Charging batteries can release hydrogen and oxygen, which may cause an explosion if ignited.
- Ensure Proper Ventilation: When charging conventional batteries, loosen the vent caps and make sure the charging area has adequate airflow. Poor ventilation may allow gases to accumulate and create a hazardous environment.
- Monitor Battery Heat: If the battery becomes hot to the touch, stop charging and allow it to cool. Overheating can damage internal plates and may cause the battery to rupture.
- Do Not Re-Seal Vent Caps: Once the red sealing cap has been removed, never replace it. Trapped gases can cause the battery to explode. Also ensure the vent tube is clear and not blocked.
- Correct Cable Connection: Always connect Positive (+) to Positive and Negative (-) to Negative.
Turn off/unplug the charger before disconnecting the leads.
Important Points to Remember
-
Keep the charging area well-ventilated
-
No smoking or open flames near charging batteries
-
Use safety goggles or face shields while handling batteries
-
If acid contacts eyes or skin, rinse immediately and seek medical help
-
Review and follow safety instructions regularly
Battery Testing Tools
To check the battery’s charge condition, use one of the following:
-
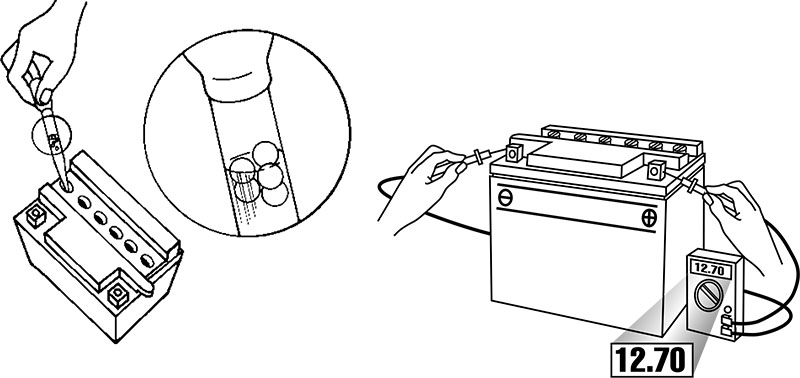
Hydrometer:
Best used on conventional batteries. Choose a calibrated float type hydrometer for more accurate specific gravity readings. -
Voltmeter / Multimeter:
Suitable for testing sealed VRLA / SMF batteries. Measures DC voltage to determine battery state.
Testing with a Voltmeter
-
Make sure the voltmeter is set to DC mode
-
Connect the meter in parallel to the battery terminals
-
Observe correct polarity to avoid reverse pointer movement
It is recommended to periodically cross-check your voltmeter with another accurate meter to ensure reliability.
Types of Battery Testing
Battery condition can be evaluated in two ways:
-
Unloaded Testing
-
Loaded Testing
Unloaded Testing is performed without applying any discharge load to the battery. It is the simplest and most common method.
For a more accurate and reliable analysis, especially when confirming battery health under working conditions, Loaded Testing is recommended.
Unloaded Testing Procedure
You can check the charge condition using either a Voltmeter or a Hydrometer:
Using a Voltmeter
-
Connect the positive lead of the voltmeter to the battery’s positive (+) terminal
-
Connect the negative lead to the negative (-) terminal
-
The voltmeter will display the battery’s voltage instantly, indicating its state of charge
Using a Hydrometer
-
A hydrometer measures the specific gravity of the electrolyte in each cell
-
Specific gravity directly indicates the battery’s charge level
Typical Readings:
| Charge Level | Specific Gravity Reading |
|---|---|
| Fully Charged | 1.265 – 1.280 |
| Needs Charging | 1.230 – 1.260 |
A reading below 1.230 generally means the battery should be charged before further testing.
Comparing Methods
Different tools may show the state of charge differently:
-
Syringe Float Hydrometer
-
Digital Voltmeter
-
Five Ball Hydrometer
Each provides useful results, but digital voltmeters are most convenient and are required for sealed VRLA / SMF batteries, where electrolyte cannot be accessed.
| State of Charge | Syringe Hydrometer | Digital Voltmeter | 5-Ball Hydrometer |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100% Charged w/Sulfate Stop |
1.280 | 12.80v | 5 Balls Floating |
| 100% Charged | 1.265 | 12.60v | 4 Balls Floating |
| 75% Charged | 1.210 | 12.40v | 3 Balls Floating |
| 50% Charged | 1.160 | 12.10v | 2 Balls Floating |
| 25% Charged | 1.120 | 11.90v | 1 Balls Floating |
| 0% Charged | less than 1.100 | less than 11.80v | 0 Balls Floating |
